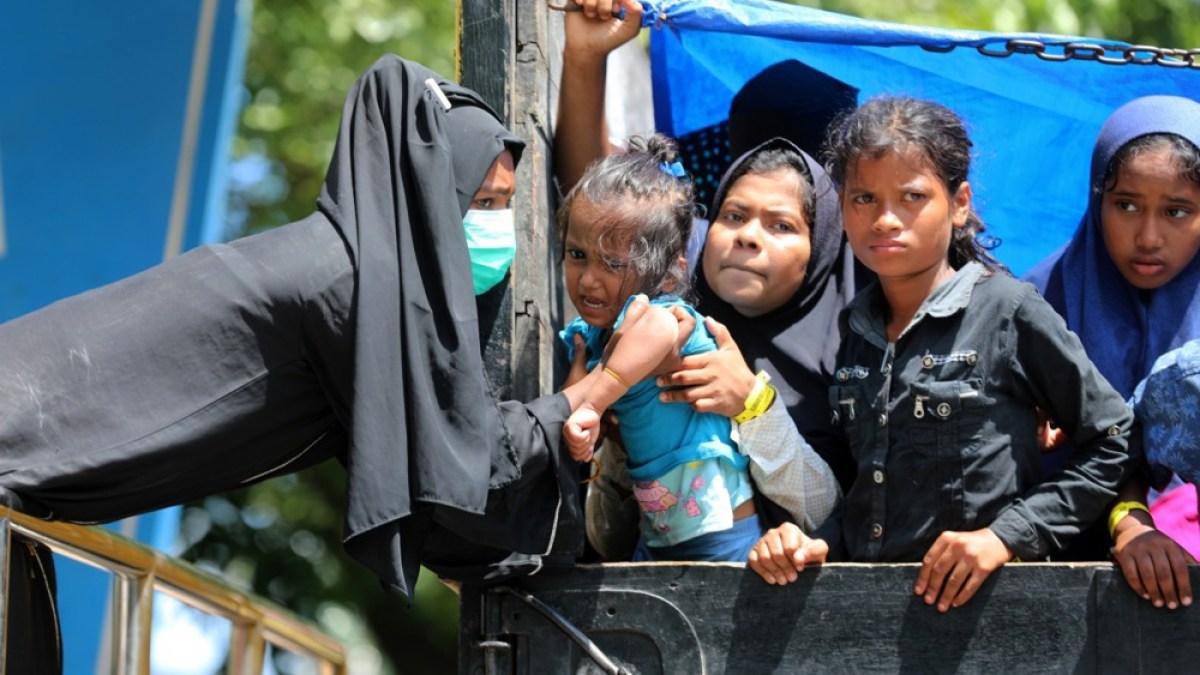
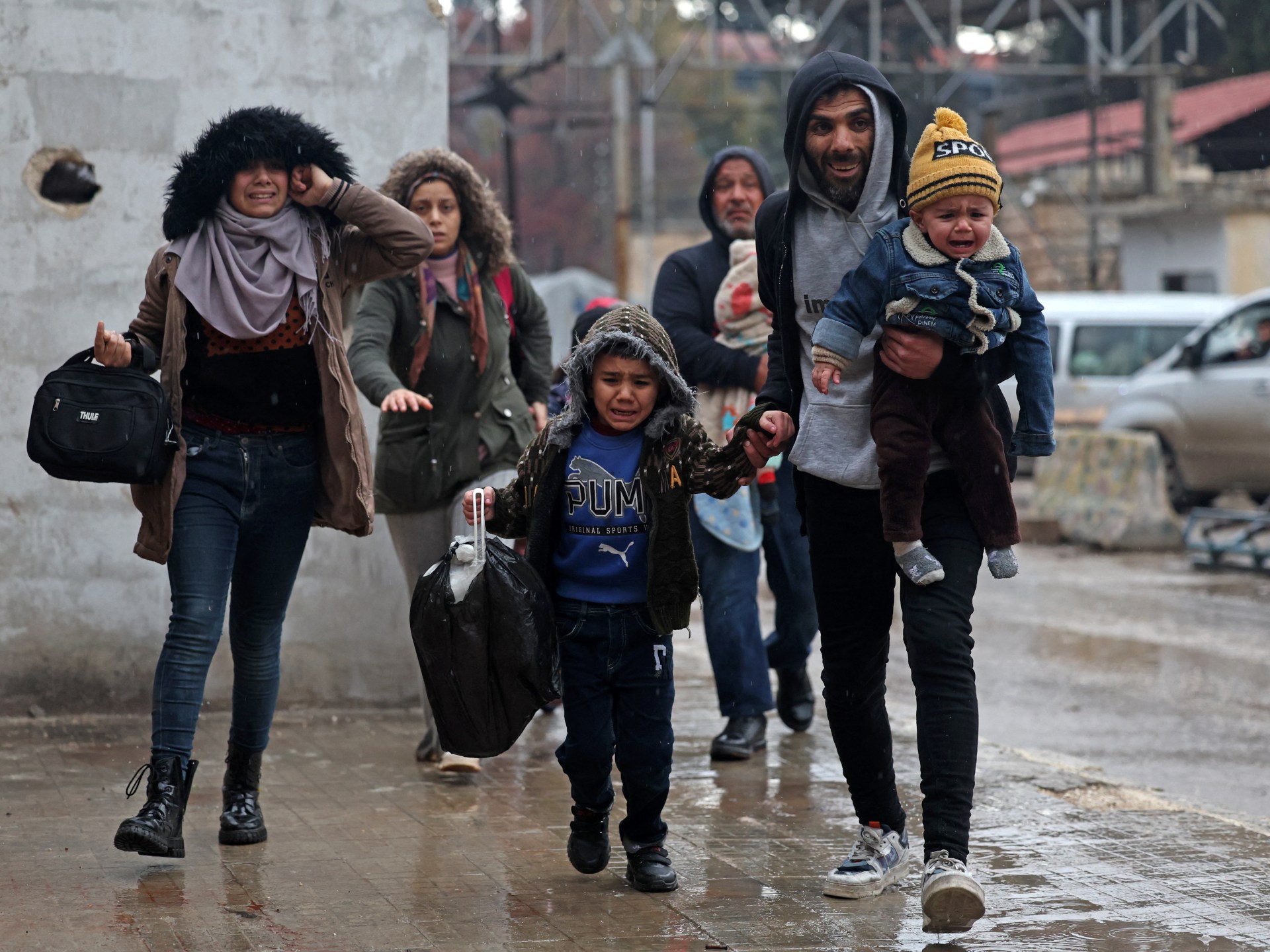

The United Nations’s top court is set to open a landmark case accusing Myanmar of committing genocide against its mostly Muslim Rohingya minority.
The trial on Monday is the first genocide case that the International Court of Justice (ICJ) will take up in full in more than a decade, and its outcome will have repercussions beyond Myanmar, likely affecting South Africa’s petition against Israel over its genocidal war on Gaza.
- list 1 of 4Malaysia recovers more bodies from capsized Rohingya refugee boat
- list 2 of 4Refugee boat sinks near Malaysia, Thailand; 21 dead, search continues
- list 3 of 4Trump administration ends temporary immigration status for Myanmar citizens
- list 4 of 4Myanmar military says armed groups used hospital it bombed, killing dozens
end of list
The hearings will start at 09:00 GMT on Monday and span three weeks.
The Gambia filed the case against Myanmar at the ICJ, also known as the World Court, in 2019, two years after the country’s military launched an offensive that forced some 750,000 Rohingya from their homes and into neighbouring Bangladesh.
The refugees recounted mass killings, rape and arson attacks.
A UN fact-finding mission at the time concluded that the 2017 offensive had included “genocidal acts”. But authorities in Myanmar rejected the report, saying its military offensive was a legitimate counterterrorism campaign in response to attacks by alleged Rohingya armed groups.
“The case is likely to set critical precedents for how genocide is defined and how it can be proven, and how violations can be remedied,” Nicholas Koumjian, head of the UN’s Independent Investigative Mechanism for Myanmar, told the Reuters news agency.
‘Renewed hope’
In Bangladesh’s Cox’s Bazar, Rohingya refugees said they hoped the genocide case would help bring justice.
“We want justice and peace,” said 37-year-old Janifa Begum, a mother of two. “Our women lost their dignity when the military junta launched the eviction. They burned villages, killed men, and women became victims of widespread violence.”
Advertisement
Others said they hoped the case would bring them real change, even though the ICJ has no way to enforce any judgement it might make.
“I hope the ICJ will bring some solace to the deep wounds we are still carrying,” said Mohammad Sayed Ullah, 33, a former teacher and now a member of the United Council of Rohingya, a refugee organisation.
“The perpetrators must be held accountable and punished,” he said. “The sooner and fairer the trial is, the better the outcome will be… then the repatriation process may begin.”
Wai Wai Nu, the head of Myanmar’s Women’s Peace Network, said the start of the trial “delivers renewed hope to Rohingya that our decades-long suffering may finally end”.
“Amid ongoing violations against the Rohingya, the world must stand firm in the pursuit of justice and a path toward ending impunity in Myanmar and restoring our rights.”
The hearings at the ICJ will mark the first time that Rohingya victims of the alleged atrocities will be heard by an international court, although those sessions will be closed to the public and the media for sensitivity and privacy reasons.
“If the ICJ finds Myanmar responsible under the Genocide Convention, it would mark a historic step in holding a state legally accountable for genocide,” said Legal Action Worldwide (LAW), a group that advocates for Rohingya rights.
Separate ICC case
During the preliminary hearings in the ICJ case in 2019, Myanmar’s then-leader, Aung San Suu Kyi, rejected The Gambia’s accusations of genocide as “incomplete and misleading”. She was later toppled by the military in a coup in 2021.
The power grab plunged Myanmar into chaos, with the military’s violent crackdown on pro-democracy protests sparking a nationwide armed rebellion.
While Myanmar’s military continues to deny the accusations of genocide, the opposition National Unity Government (NUG), established by elected lawmakers after the 2021 coup, said it has “accepted and welcomed” the jurisdiction of the ICJ, adding that it has “withdrawn all preliminary objections” previously submitted on the case.
In a statement ahead of the hearing, the NUG acknowledged the government’s failures, which it said “enabled grave atrocities” to take place against minority groups. It also acknowledged the name Rohingya, which the previous elected government, including Aung San Suu Kyi, had refused to do.
“We are committed to ensuring such crimes are never repeated,” the NUG said.
Myanmar’s military leader, Senior General Min Aung Hlaing, is facing a separate arrest warrant before the International Criminal Court (ICC) for his role in the persecution of the Rohingya.
Advertisement
The ICC prosecution said the general “bears criminal responsibility for the crimes against humanity of deportation and persecution of the Rohingya, committed in Myanmar, and in part in Bangladesh.”
Additionally, the Burmese Rohingya Organisation UK (BROUK) has accused the military government of “intensifying genocide” against the Rohingya since taking power in 2021.
Myanmar is currently holding phased elections that have been criticised by the UN, some Western countries and human rights groups as not free or fair.
Related News
Russia-Ukraine war: List of key events, day 1,414

New video on Minnesota ICE shooting emerges as public anger grows across US
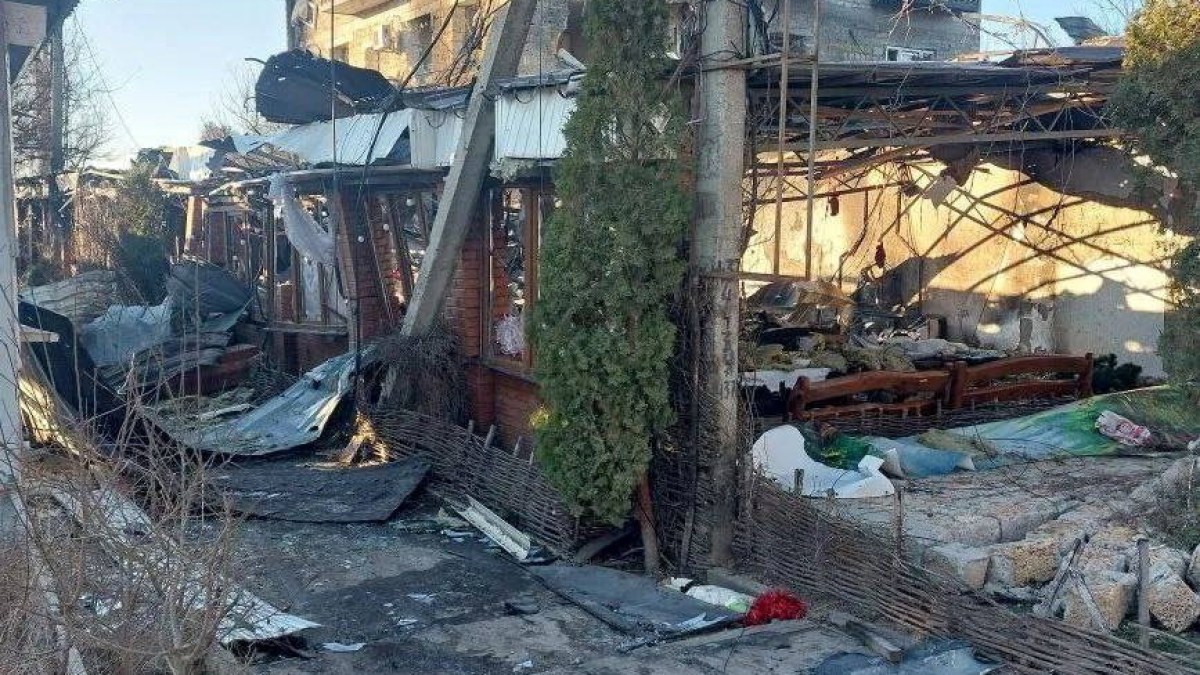

Russia claims Ukrainian drone attack killed 24 people in Kherson


